The historical analysis presented in “Nelson’s Battles in 3D: Trafalgar” encapsulates the critical maritime confrontation that unfolded in 1805 during the Napoleonic Wars. It examines the geopolitical backdrop wherein Napoleon Bonaparte aimed to establish dominance over Britain, necessitating the defeat of a coalition comprising Britain, Russia, and Austria. The video portrays Admiral Horatio Nelson, the audacious commander of the British fleet, who, despite being outnumbered, devised innovative tactics to engage the formidable Combined Fleet of French and Spanish ships.
Key events leading to the Battle of Trafalgar are meticulously outlined, highlighting the strategic maneuvers and missteps of both the British and French-Spanish forces. The video captures the intensity of the October 21 confrontation, illustrating Nelson’s unconventional tactics that ultimately secured a decisive victory for Britain. The aftermath of the battle not only solidified British naval supremacy for years to come but also immortalized Nelson as a national hero, despite the personal sacrifice he endured during this historic engagement.
Historical Context
Napoleon’s Strategic Aims
In the early 19th century, the geopolitical landscape of Europe was profoundly shaped by the aspirations of Napoleon Bonaparte. Following the dissolution of the Treaty of Amiens in 1803, which had briefly halted hostilities between Britain and France, Napoleon strategized a formidable plan to invade Britain. His ambition hinged on defeating the Third Coalition—a formidable alliance consisting of Britain, Russia, and Austria—prior to launching a cross-Channel invasion. To realize this objective, he recognized that the primary obstacle was the British Royal Navy, the epitome of naval power at the time that had established maritime supremacy for over a century.
Notably, Napoleon sought to leverage a concentrated force to achieve temporary dominion over the English Channel, thereby allowing his large and experienced army to land on British soil. He understood well that military engagements on land would only bear fruit if the sea could be navigated without threat from the British fleet. This led him to form alliances and consolidate the naval strength of France and Spain, with a focus on disrupting British maritime commerce and influencing the outcome of the ongoing conflict.
The Third Coalition Against France
The establishment of the Third Coalition marked a significant phase in the Napoleonic Wars. Primarily formed in response to Napoleon’s expansionist policies, the coalition united Britain, Russia, Austria, and other nations against French hegemony. This amalgamation of power was intended to curtail the incessant threats posed by Napoleon, who had demonstrated formidable military abilities and a penchant for rapid advancements across Europe.
At the heart of this alliance was an understanding that the defeat of the French army could only be achieved by confronting Napoleon on multiple fronts. To succeed, the allied forces intended to employ coordinated military strategies that spanned the continent, leading to campaigns in Central and Eastern Europe. The focus, however, remained on dismantling Napoleon’s formidable army, primarily through interventions that would disrupt his supply lines and weaken his naval capabilities.
The Role of the Royal Navy
The Royal Navy emerged as the bedrock of British military strength during this tumultuous era. Its superiority was not merely a matter of naval tactics but also stemmed from an extensive logistical network, technological advancement, and a tradition of aggressive engagement on the high seas. The British fleet dominated trade routes and was adept at blockading enemy ports, thereby stemming economic resources crucial for warfare.
Given Napoleon’s intentions to invade Britain, the Royal Navy stood as a formidable barrier, representing not only a military challenge but also a psychological one. Its capability to control the Atlantic and the English Channel meant that any French invasion plan required a counterbalance to the power wielded by British naval commanders like Admiral Horatio Nelson. The ensuing battles would illustrate the pivotal role the Royal Navy played in shaping the fate of nations during the Napoleonic Wars, particularly at the Battle of Trafalgar.
Admiral Nelson’s Leadership
Background and Career
Admiral Horatio Nelson emerged as a pivotal figure in the narrative of British naval dominance, characterized by his unconventional tactics and inspiring leadership. Born on September 29, 1758, in Norfolk, England, Nelson’s naval career began at an early age when he joined the British Navy at just 12 years old. Over the years, he accrued a wealth of experience and rapidly ascended through the ranks, demonstrating a particular aptitude for commanding ships in battle.
Nelson’s prior engagements, including the successful Battle of the Nile in 1798 against the French, established him as a naval tactician of extraordinary caliber. His ability to lead under pressure and devise strategies that exploited the enemy’s vulnerabilities became hallmarks of his command style. By the time of the Battle of Trafalgar in 1805, Nelson had built a reputation not just as a tactician but as a charismatic leader who inspired unwavering loyalty among his crew.
Tactical Innovations
One of the most significant contributions of Admiral Nelson to naval warfare lay in his strategic innovations. He transcended traditional tactics that favored linear formations and movement, opting instead for unconventional strategies that rendered the conventional “line of battle” ineffective against well-trained adversaries. His plan at Trafalgar, which involved dividing his fleet and attacking the enemy in two columns to disrupt their battle line, heralded a new era in naval tactics.
Nelson’s approach highlighted the importance of speed and surprise, which he deemed critical to achieving victory. His willingness to take calculated risks set him apart from his contemporaries, which he often justified through the need to conserve lives while inflicting maximum damage on enemy vessels. Moreover, his foresight in understanding the psychological components of naval engagements enabled him to tailor his tactics to not only confront threats but to demoralize foes effectively.
Personal Charisma and Inspiration
Nelson’s magnetic personality played an essential role in fostering dedication and tenacity among his crew members. His innate ability to connect with sailors and officers alike created a cohesive unit that thrived under pressure. This was particularly evident in his famous motto, “England expects that every man will do his duty,” signaled prior to the Battle of Trafalgar, which imbued the fleet with a sense of purpose and responsibility.
His personal charisma was palpable; he garnered steadfast loyalty not through fear but through shared ideals of courage, honor, and duty. This emotional connection facilitated a fighting spirit within his fleet, allowing them to trust his judgment in moments of peril. Furthermore, his adeptness at recognizing and cultivating talent among his officers created an environment of mutual respect, where innovation and initiative were valued. As a result, Admiral Nelson’s leadership resonated profoundly, leading to unparalleled feats of bravery during some of the most critical battles of the Napoleonic Wars.

Battle Preparations
Formation of the Combined Fleet
In the lead-up to the Battle of Trafalgar, the strategic collaboration between France and Spain culminated in the formation of a formidable Combined Fleet. This alliance arose from the urgent need to challenge British dominance at sea, with French Admiral Pierre Villeneuve tasked with leading the naval force. The Combined Fleet was composed of 33 ships of the line—18 French vessels and 15 Spanish vessels—aiming to counter the British fleet currently commanded by Admiral Nelson.
The consolidation of naval forces was fraught with challenges, as historical rivalries and the coordination of two distinct naval traditions demanded skillful management and leadership. Villeneuve’s command was set against a backdrop of high expectations, yet the internal complexities within the coalition presented obstacles to effective collaboration. The collective ambition underscored the need for unity, even as disparate maritime doctrines and cultural differences came into play.
Command Structure under Villeneuve
The command structure of the Combined Fleet rested upon Admiral Villeneuve’s leadership, with Vice Admiral Federico Gravina commanding the Spanish contingent. However, Villeneuve’s leadership was marred by indecisiveness and tactical missteps, which diminished the fleet’s operational effectiveness. His preference for a cautious approach contrasted sharply with Nelson’s aggressive tactics.
Despite his experience, Villeneuve struggled to inspire confidence in his subordinates, which compounded the difficulties inherent in coordinating fleet movements. Moreover, tensions within the command structure stymied prompt decision-making and unity of purpose. This disarray proved detrimental, particularly as tensions escalated and the British fleet, under the capable leadership of Admiral Nelson, began to close in on the Combined Fleet.
Logistical Challenges Faced
The logistical framework underpinning the Combined Fleet’s operations was characterized by intricate challenges. The sheer scale of coordinating multiple ships and their respective crews, each with separate strategies and operational protocols, posed significant difficulties. Conditions at sea were further complicated by the need to supply and maintain ships amid adverse weather and limited resources.
Villeneuve’s inability to consolidate his forces and his subsequent retreat to Cadiz from initial engagements further exacerbated the logistical predicament. The ports’ over-crowding and declining morale among sailors created an environment where effective naval maneuvers were increasingly elusive. Ill-prepared and struggling with inadequate provisions, the Combined Fleet found itself at a disadvantage, setting the stage for imminent confrontation with the British Navy.
Key Events Leading to Trafalgar
Failed French Operations
The events leading up to the Battle of Trafalgar were marked by a series of miscalculations and failed operations on the part of the French Navy. Admiral Villeneuve’s attempts to engage the British fleet were hampered by a lack of decisive action and effective leadership, leading to missed opportunities in confronting Nelson’s forces. His retreat to Cadiz, rather than advancing toward combat, significantly undermined Napoleon’s strategic objectives.
The French operations were further complicated by internal discord within the fleet. Mixed signals and divergent strategies fueled disarray, as rivalries between commanders culminated in tactical blunders. Such failures served to embolden British naval engagements, providing them insight into Villeneuve’s operational patterns and weaknesses, which they would exploit at Trafalgar.
British Intelligence and Tracking
In stark contrast, British naval intelligence emerged as a pivotal asset in the run-up to the conflict at Trafalgar. The Royal Navy’s extensive network of espionage and reconnaissance enabled Admiral Nelson to track the movements of the Combined Fleet with remarkable accuracy. British ships scoured the Atlantic and the Mediterranean, gathering intelligence that would inform Nelson’s strategic decisions.
This intelligence not only allowed the British to anticipate the actions of their foes but also enhanced their operational readiness. Nelson’s preparations, bolstered by accurate data about enemy numbers and formations, placed the British fleet in a position of tactical advantage. This emphasis on intelligence gathering was emblematic of Britain’s broader military prowess, underscoring the importance of foresight in naval engagements.
Pre-Battle Tensions
As tensions mounted leading up to the fateful day of Trafalgar, both the British and French navies found themselves on high alert. For Nelson, the psychological toll of knowing he would engage a numerically superior opponent weighed heavily on command dynamics. Despite being outnumbered, he instilled a sense of urgency and confidence within his fleet, urging them to rise to the occasion.
Conversely, Villeneuve felt the pressure of expectations from both Napoleon and his own officers, exacerbated by prior failures. The looming threat of engagement heightened uncertainties in command, as both fleets braced for what would become a landmark battle. The focus was sharpened on either side, culminating in a frenzied countdown to their inevitable confrontation on October 21, 1805.
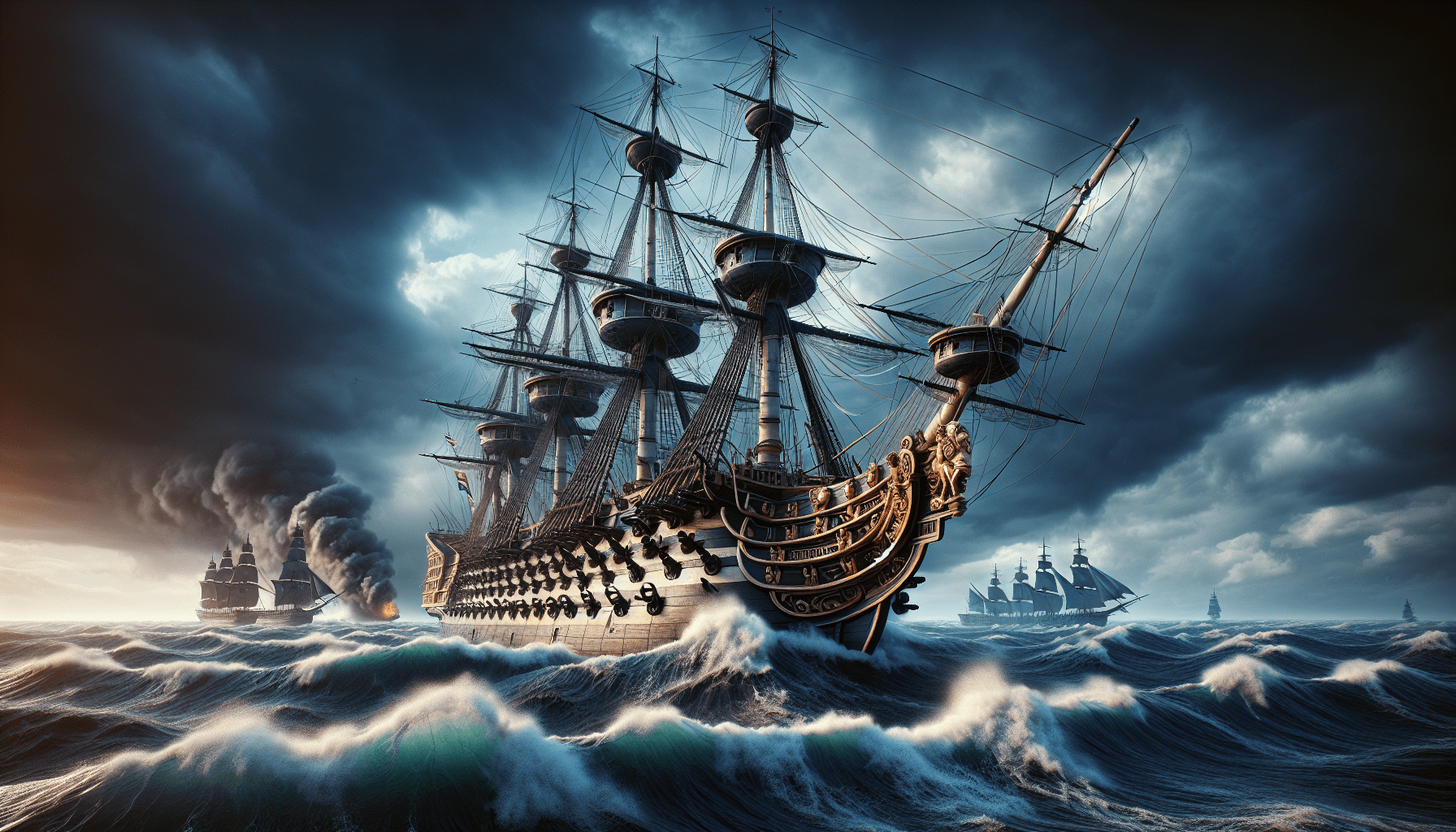
Battle of Trafalgar
Initial Engagement and Tactics
The Battle of Trafalgar commenced on October 21, 1805, as the British fleet, numbering 27 ships, encountered the Combined Fleet’s 33 vessels off the southern coast of Spain. The initial engagement involved British ships advancing slowly toward the enemy lines, impeded by light winds that created a tense atmosphere. In an aggressive display of naval strategy, Admiral Nelson signaled his famous battle order, which emphasized the need for each sailor to perform their duty with unwavering resolve.
The British ships engaged in a 45-minute bombardment before reaching enemy lines, setting the stage for a complex series of maneuvers that would test their tactical prowess. Villeneuve’s fleet, concentrated in a linear formation, aimed to outnumber the British but was unprepared to counter Nelson’s innovative tactics.
Nelson’s Strategy of Attack
Nelson’s strategy at Trafalgar showcased a daring departure from conventional approaches to naval warfare. He resolved to breach the Combined Fleet’s battle line by splitting his forces into two attacking columns, aiming to disrupt the enemy’s cohesion. This tactic was predicated on the idea that the British fleet’s superior training and morale could overcome numerical disadvantages.
His focus was on targeting Villeneuve’s flagship, Bucentaure, and disabling key enemy units to create chaos within their ranks. By engaging the enemy at close quarters, Nelson aimed to maximize the efficiency of his crew and ships, enabling them to inflict significant damage. His unyielding audacity embodied the very spirit of British naval tradition, setting a precedent for subsequent engagements while establishing his tactical legacy.
The Role of Vice Admiral Collingwood
Vice Admiral Cuthbert Collingwood played an integral role during the Battle of Trafalgar, complementing Nelson’s strategic vision with his own expertise and leadership qualities. Commanding the HMS Royal Sovereign, Collingwood’s ship was among the first to engage the enemy, breaking their line and delivering heavy fire against enemy vessels.
His actions during the battle were instrumental in the British victory, as he rallied ships and coordinated attacks amid the chaos. Collingwood’s presence galvanized the British fleet, emphasizing the importance of collective effort in executing the intricate plan devised by Nelson. In the wake of the conflict, Collingwood assumed command of the fleet following Nelson’s mortal wounding, demonstrating his capacity for leadership under pressure in the face of adversity.
Outcomes of the Battle
Casualties and Damage Assessment
The outcomes of the Battle of Trafalgar were decidedly in favor of the British, marking a historic moment in naval tradition. The British fleet suffered significantly lower casualties than their French and Spanish counterparts, with around 480 men lost compared to an estimated 4,400 casualties among the Combined Fleet. The overwhelming tactical advantage wielded by Nelson and Collingwood, coupled with the prowess of British sailors, rendered the decisive victory even more pronounced.
Damage assessments revealed substantial losses for the Combined Fleet, with many French and Spanish ships destroyed or captured. The British fleet’s superior gunnery and aggressive tactics enabled them to inflict heavy blows, leaving Villeneuve’s forces dismantled and demoralized. This engagement not only crippled the Combined Fleet but also solidified British naval supremacy for the years to come.
Capture and Destruction of Enemy Ships
The Battle of Trafalgar resulted in a significant navigation of fate, with 22 enemy vessels either captured or sunk in the aftermath. This staggering loss for the French and Spanish fleets effectively dismantled their capacity to challenge British dominance at sea. The vigorous assaults executed by the British forces ensured that few ships escaped the fervor of the battle.
Among the most notable captures were several high-ranking French and Spanish vessels that had previously foreshadowed a formidable opposition. The loss of these ships would shape naval conflicts in subsequent engagements, as Britain could reclaim not just dominance but also boast a bolstered naval reputation across Europe.
Long-term Impacts on Naval Warfare
The ramifications of the Battle of Trafalgar echoed well beyond its immediate outcomes. British naval command solidified post-battle, ushering in a period of unmatched maritime control over the seas. This decisive victory emphasized the tactical innovations introduced by Nelson, establishing new standards for naval warfare that emphasized agility, surprise, and assertive engagement.
Admiral Nelson’s legacy further resonated across naval strategies, as maritime powers worldwide reevaluated their operational paradigms. The defeat at Trafalgar rendered the French navy incapable of effective action against the British, essentially shifting the balance of power in favor of Britain, and marking a transformational epoch in naval history.
Significance of Trafalgar
Establishment of British Naval Supremacy
The Battle of Trafalgar achieved a watershed moment for British naval supremacy, cementing its position as the unrivaled naval power of the 19th century. Following the battle, the Royal Navy asserted control over the vast majority of maritime routes, giving Britain the ability to dominate global trade and military engagements. This supremacy facilitated the expansion of the British Empire, allowing it to extend its influence across continents.
The victory at Trafalgar ensured that Britain could intervene in conflicts globally without fear of being challenged at sea. This period of maritime dominance solidified Britain’s role as the world’s preeminent imperial power, fostering economic growth and international influence that would last for decades.
Nelson as a National Hero
Admiral Horatio Nelson’s status as a national hero burgeoned following the Battle of Trafalgar. His valiant leadership, strategic brilliance, and ultimate sacrifice captivated the British public, inspiring a wave of nationalism. Nelson became emblematic of British maritime strength, transcending his military role to symbolize the indomitable spirit of the nation.
Despite his death during the battle, Nelson’s legacy lived on, his example resonating through the naval tradition and beyond. Statues and memorials commemorating his achievements were established, entrenching him in the annals of British history as a poignant figure whose heroism and tactical innovations would be celebrated for generations.
Influences on Global Power Dynamics
The repercussions of Trafalgar rippled through global power dynamics, altering the calculus of European alliances and confrontations. With French naval power severely diminished, Britain emerged as the uncontested leader in maritime affairs. The battle contributed to a reconfiguration of European alliances, with nations reconsidering their positions in relation to an assertive British Empire.
As conflicts continued, the consequences of Trafalgar reverberated through subsequent engagements, impacting the strategies adopted by emerging naval powers. The British method of naval warfare became a benchmark for others, leading to adjustments in ship design, tactical formations, and training regimens across the globe. This battle would thus serve as a reference point for future naval conflicts, molding the evolution of maritime strategy.
Aftermath of the Battle
Weather and Its Impact on the British Fleet
In the wake of the triumphant battle, the British fleet encountered unforeseen challenges posed by inclement weather. The severity of the Atlantic storm soon after Trafalgar scattered the victorious ships, complicating the logistics of dealing with captured vessels and the care of injured crew members. While the storm had minimal impact on the morale of the British forces, it hindered the immediate consolidation of victory that would have otherwise been celebrated.
The adverse weather also led to logistical difficulties as ships navigated treacherous conditions, further cementing the complexities of naval warfare beyond mere combat. Many captured enemy vessels were forced to contend with the tempest, illustrating the ongoing struggles that were part and parcel of maritime endeavors during this period.
Return of Nelson’s Body and Statues
The death of Admiral Nelson marked a profound moment of national mourning in Britain. His body was preserved and transported back to England in a cask of brandy, reflecting the honor bestowed upon him as a fallen hero. Nelson’s state funeral was held in London, attended by thousands, capturing the collective grief and reverence felt across the nation.
Furthermore, his contributions were immortalized through statues and monuments, standing as testament to his legendary status and the enduring legacy of the Battle of Trafalgar. Nelson’s Column, located in Trafalgar Square, serves as a prominent symbol of national pride and remembrance, grounding him in the collective consciousness of a nation forever changed by his exploits.
Continued Naval Developments
As Britain basked in the glow of its newfound supremacy, the repercussions of Trafalgar extended into naval developments and innovations. With an emphasis on the strategies and tactics employed by Nelson, the Royal Navy undertook a period of introspection and adaptation, refining its approach to training and ship design.
The emphasis on gunnery training, seamanship, and tactical astuteness became hallmarks of British naval tradition, ensuring that future commanders would be well-prepared for engagements yet to come. This focus on continual improvement not only solidified Britain’s dominance at sea but also laid down the foundations for naval warfare in the years leading to the dawn of modern naval engagements.
Epic History’s Commitment
Focus on Authenticity and Education
Epic History is committed to delivering authentic, educational content that engages audiences in a meaningful exploration of historical events. By emphasizing thorough research and a nuanced understanding of complex narratives, the organization aims to foster a deeper appreciation of history’s intricacies. The commitment to authenticity extends to the narratives that depict the multifaceted layers of human experiences during pivotal moments, such as the Battle of Trafalgar.
Research and Production Team
The production team at Epic History comprises a diverse collective of historians, researchers, and creatives dedicated to delivering reliable narratives rooted in scholarly rigor. The collaboration of experts, such as Drachinifel, elucidates the nuanced perspectives surrounding historical events and adds layers of depth to the storytelling approach utilized by the organization.
Content Creation Philosophy
Epic History’s content creation philosophy revolves around the belief that history should be accessible and engaging, marrying educational rigor with captivating storytelling. By employing storytelling techniques that resonate with audiences, Epic History aims to kindle curiosity while illuminating the significance of historical events, ensuring that viewers depart with a clearer understanding and appreciation of the past.
Conclusion
Summary of Nelson’s Legacy
Admiral Horatio Nelson’s legacy endures as a towering figure in naval history, his innovations and leadership redefining strategies in wartime naval engagements. His triumph at Trafalgar solidified his place in the pantheon of military heroes, showcasing the profound impact of exceptional leadership, tactical innovation, and selfless sacrifice. The reverberations of his actions continued to shape the course of British history and inform naval warfare for generations.
Impact of Trafalgar on History
The Battle of Trafalgar stands as a critical juncture in the narrative of European imperial power dynamics, heralding an era of British naval supremacy that would echo through the 19th century. Its influences reached far beyond the battleground, reshaping alliances, altering military strategies, and establishing Britain as an indomitable maritime force. The ramifications of this engagement have been felt in both military and economic contexts, marking a transformative epoch in the development of global power structures.
The Importance of Historical Understanding
Understanding the events surrounding the Battle of Trafalgar is fundamental in grasping the complexities of European history. The intricate interplay of alliances, military strategies, and the human experience captured in this narrative reflect the broader socio-political currents that have shaped modern societies. Historical comprehension enables deeper insights into contemporary conflicts, informing future choices while cultivating an appreciation for the enduring nature of human endeavors amidst the trials of war. Seeking to understand the past is essential in navigating the path of the future.
